Bat-inspired tiny drones could save lives
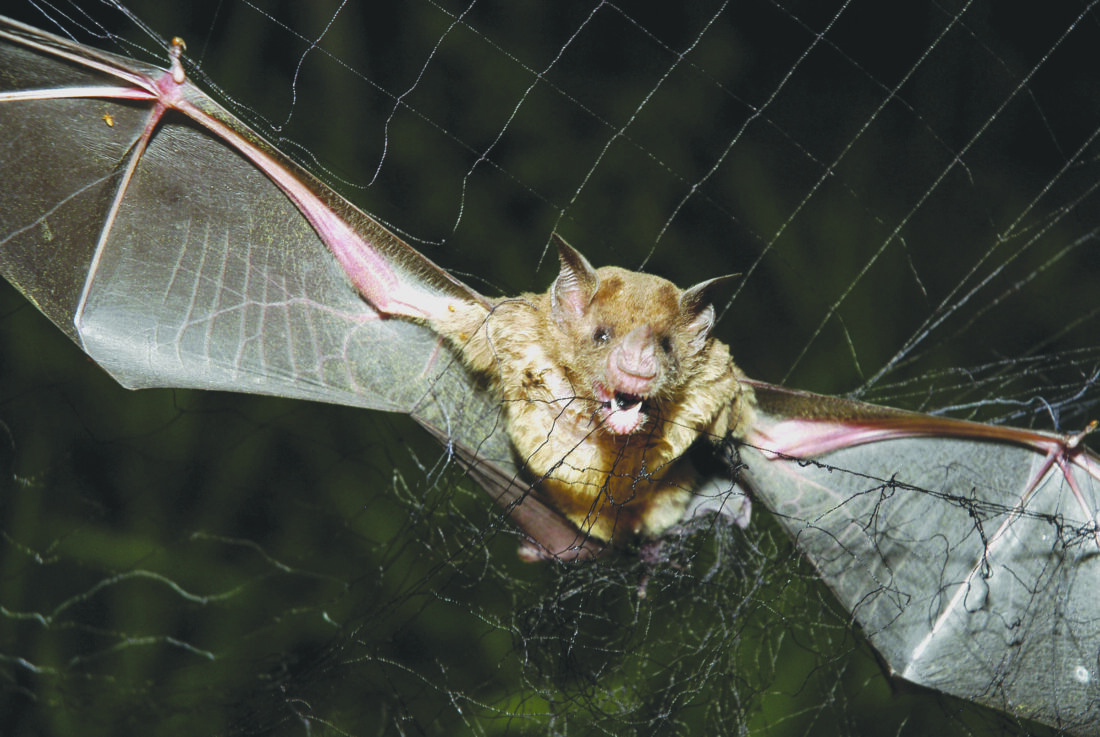

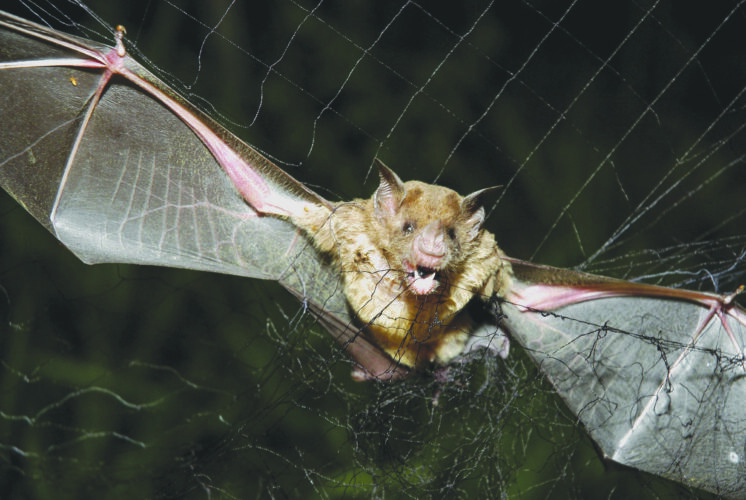
A vampire bat is caught in a net in Aracy, in the northeast Amazon state of Para, Brazil, in December 2005. (AP file photo)
WORCESTER, Mass. — Don’t be fooled by the fog machine, spooky lights and fake bats: the robotics lab at Worcester Polytechnic Institute lab isn’t hosting a Halloween party.
Instead, it’s a testing ground for tiny drones that can be deployed in search and rescue missions even in dark, smoky or stormy conditions.
“We all know that when there’s an earthquake or a tsunami, the first thing that goes down is power lines. A lot of times, it’s at night, and you’re not going to wait until the next morning to go and rescue survivors,” said Nitin Sanket, assistant professor of robotics engineering. “So we started looking at nature. Is there a creature in the world which can actually do this?”
Sanket and his students found their answer in bats and the winged mammal’s highly sophisticated ability to echolocate, or navigate via reflected sound. With a National Science Foundation grant, they’re developing small, inexpensive and energy-efficient aerial robots that can be flown where and when current drones can’t operate.
Last month, emergency workers in Pakistan used drones to find people stranded on rooftops by massive floods. In August, a rescue team used a drone to find a California man who got trapped for two days behind a waterfall. And in July, drones helped find a stable route to three mine workers who spent more than 60 hours trapped underground in Canada.
But while drones are becoming more common in search and rescue, Sanket and researchers elsewhere want to move beyond the manually operated individual robots being used today. A key next step is developing aerial robots that can be deployed in swarms and make their own decisions about where to search, said Ryan Williams, an associate professor at Virginia Tech.
“That type of deployment — autonomous drones — that is effectively nil,” he said.
Williams tackled that problem with a recent project that involved programming drones to choose search trajectories in coordination with human searchers. Among other things, his team used historical data from thousands of missing person cases to create a model predicting how someone would behave if lost in the woods.
“And then we used that model to better localize our drones, to search in locations with higher chances of finding someone,” he said.